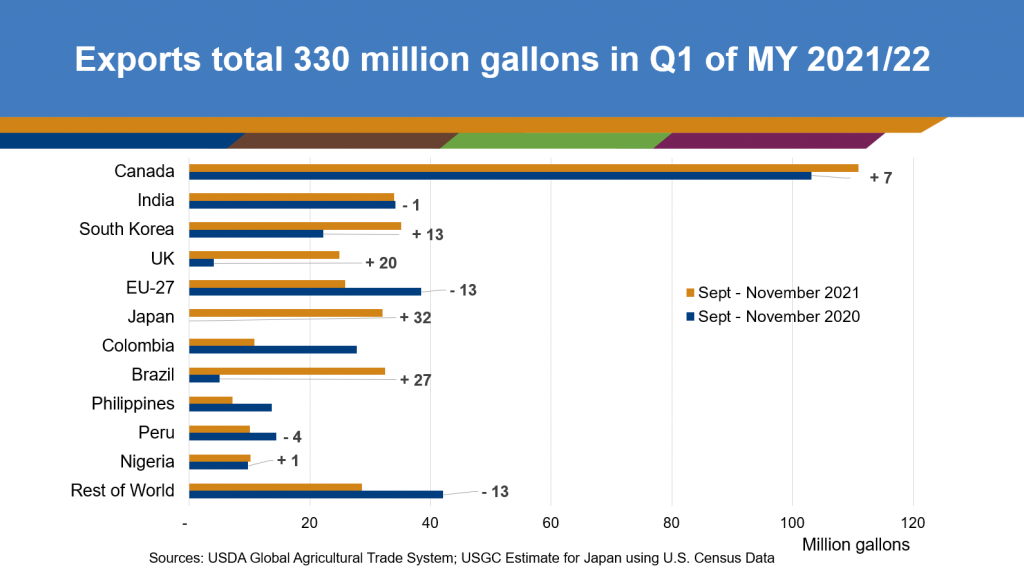
U.S. ethanol exports for the first quarter of the 2021/2022 marketing year (MY) landed five percent higher than the previous year, totaling 330 million gallons. Increased mobility and reduced COVID-19 restrictions have spurred a near global recovery in ethanol trade. Gains were seen in Brazil, and policy developments signal long term increased demand in Canada, the United Kingdom (UK), the European Union (EU), Colombia and India.
In Brazil, U.S. fuel ethanol exports saw a boost in the first quarter of this marketing year, totaling 32 million gallons, over six times more than the first period of the previous year. Following the implementation of a 20 percent tariff in December 2020, U.S. ethanol exports to Brazil remained near-zero for the remainder of the marketing year, ending MY 2020/2021 with a 200-million-gallon shortfall compared to the previous year. After a challenging crop year, Brazil is beginning to re-enter the market for U.S. ethanol to meet its blending mandates.
“Trade is the mechanism for countries to meet their policies, so this uptick is encouraging in this first quarter,” said Isabelle Ausdal, U.S. Grains Council (USGC) manager of ethanol trade policy and economics. “The removal of this and all tariffs remains a priority globally.”
In Canada, fuel ethanol was slightly higher than last year, as drivers continued to return to the road. Policies such as the national Clean Fuel Standard (CFS) and provincial policies including Quebec’s low carbon fuel standard and E15 in Ontario are expected to drive further demand for ethanol in that market. Final CFS legislation is expected to be published in Spring 2022. Quebec’s new standard will require 10 percent renewable content in gasoline by 2023 and 15 percent by 2030 in alignment with Quebec’s 2030 Plan for a Green Economy. Ontario will require 15 percent ethanol blending in gasoline by 2030 and will directly increase blending in Canada’s most populous province. The two provinces account for roughly 55 percent of fuel demand in Canada.
“According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), U.S. ethanol on average decreases greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by over 50 percent compared to traditional gasoline and provides countries with tangible progress toward their GHG reduction goals,” Ausdal said.
Exports to the EU and UK totaled 58 million gallons for the first quarter of the 2021/2022 marketing year as drivers also returned to the road in those markets. In the UK, the Renewable Fuel Transport Obligation (RTFO) officially came into force on Jan. 1, 2022, boosting the national blend mandate implemented in September 2021 and providing additional GHG reductions. Implementation of the RTFO may increase the national blending average to eight percent. In the EU, member states are beginning to incorporate the requirements of the RED II Directive into their national legislation, requiring at least 14 percent renewable energy in the transport sector by 2030. This includes increased blending of biofuels such as ethanol. The launch of E10 in Sweden and higher blending rates in France and Germany are also expected to increase EU demand in 2022.
In Colombia, the reinstatement of Colombia’s E10 mandate was postponed for a second time and is now expected to occur in August 2022. As a result, demand was down more than 50 percent in the first quarter of this marketing year compared to the last year.
Industrial ethanol exports to South Korea in the first three months of this marketing year experienced a notable boost, totaling 35 million gallons, two times higher than last year. Exports to India remained nearly equal, with the bulk of exports occurring in the last two months.
“The Council is encouraged by this uptick in global ethanol trade,” said Brian Healy, USGC director of global ethanol market development. “Our offices are hard at work with local partners in demonstrating the ongoing value of using globally available, low carbon ethanol to meet their policy goals.”
About The U.S. Grains Council
The U.S. Grains Council develops export markets for U.S. barley, corn, sorghum and related products including distiller’s dried grains with solubles (DDGS) and ethanol. With full-time presence in 28 locations, the Council operates programs in more than 50 countries and the European Union. The Council believes exports are vital to global economic development and to U.S. agriculture’s profitability. Detailed information about the Council and its programs is online at www.grains.org.