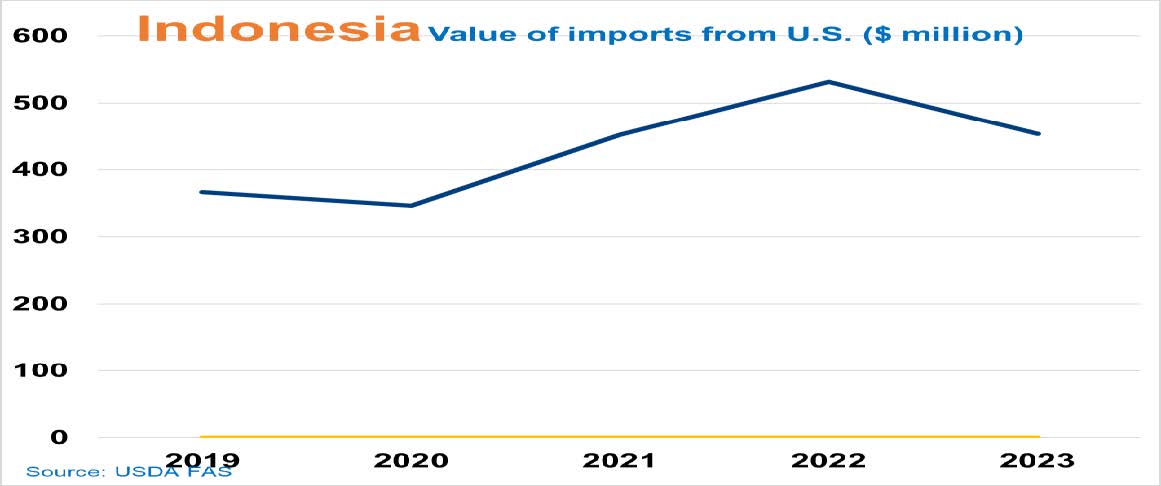
Supply/Demand Basics
-Southeast Asia’s largest importer of U.S. CGM/CGF, importing 169 TMT MY 2022/2023
-4th largest importer of U.S. DDGS, importing837 TMTin MY 2022/2023
-2023 local corn prices are among the most expensive globally due to supply constraints
-Feed mill production capacity of 29.7 MMT, with utilization at 70-75% capacity
-Wheat imports for MY 2022/2023 are estimated to decrease to 9 MMT from 11.23 MMT due to lower demand
Country Overview
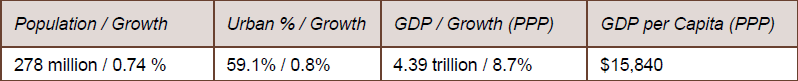
-Largest gross domestic product in SoutheastAsia; 4th largest population in the world
-GDP growth is expected to grow by 5% in 2023 (Bank Indonesia)
-An archipelago country of 17,500 islands creates massive infrastructureand logistics headwinds
-Largest Islamic country in the world, with 87% of the population Muslim.
Trade and Market Share Overview
-Southeast Asia’slargest corn grower, producing 12.9 MMT in 2023.
-Poultry industry consumes about 90% domestic animal feed volume; aqua (6%) and cattle and swine (4%) consume the balance
-Increased wet mill capacities and new ethanol plants are estimated to increase MY 2022/2023 corn imports to 1.2 MMT as compared to 1.165 MMT in the previous year
-Poultry consumption per capitais estimated to hit 8.54 kg in 2024 and steadilyincrease to 9.3 kg in 2029
Policy Overview
-Indonesia’s state food procurement agency,BULOG, was assigned to import 500kmt of corn for animal feed in October 2023 due to lower domestic output.
-Government targets corn imports of 1.34 MMT of corn by the end of 2023.
-BULOG (central desk) to hold a national monopoly on corn importation.Established the National Food Agency (BPN) to implement policies related tofood availability .
-State Owned Oil Company restricts ethanol inclusion in imported gasoline to 3% (5% 2023 pilot program underway).
-Tariffs: 5% Corn (restricted for industrial use), 5% CGM/CGF/DDGS, 30% Ethanol.