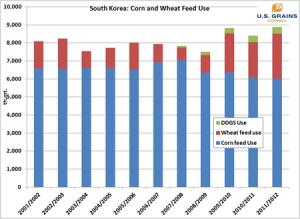
South Korea is one of the best examples of how high commodity prices encourage the search for alternative feed ingredients.
The columns in blue show total Korean corn feed use (all imported) over the past decade, rising to 7 million metric tons (278.6 million bushels) in 2007/2008 and declining to 6 million tons (236.2 million bushels) in 2011/2012. But that decline in corn use is more than compensated for by increases in wheat feeding and distiller’s dried grains with solubles (DDGS) imports.
In 2011/2012 imports of corn, feed wheat and DDGS are projected to be 8.9 million tons. The U.S. share of Korea’s corn imports is variable, but has risen over the decade from 12 percent in 2001 to 75 percent last year. Korea is one of the top export markets for U.S. DDGS, the fifth-largest market in 2010/2011.